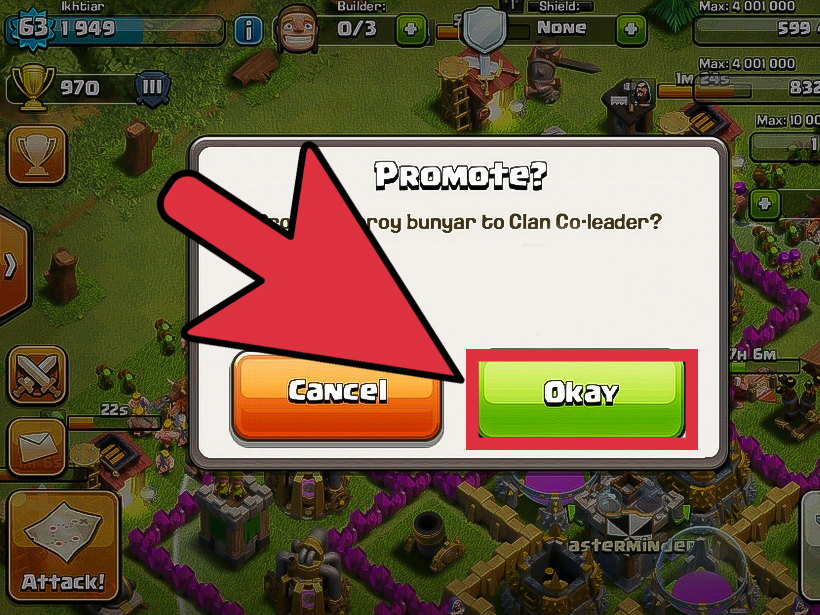
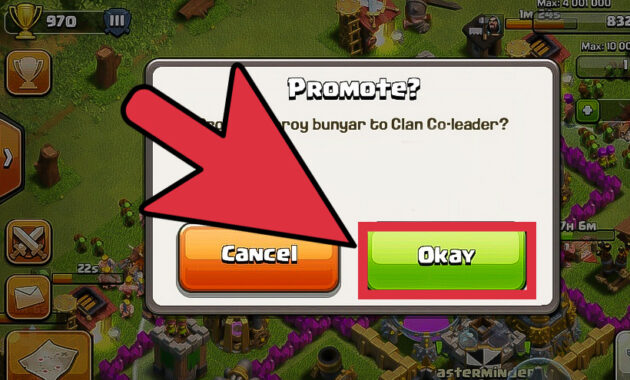
How to Optimize Your Phone for High-Performance Gaming opens the door to a realm where mobile devices can unleash their fullest potential, transforming casual gameplay into an exhilarating experience. As mobile gaming continues to rise in popularity, players seek ways to enhance their devices, ensuring seamless performance and responsiveness. This exploration delves into practical strategies and innovative techniques that can elevate gaming experiences, addressing the growing demand for high-performance functionality in smartphones.
From adjusting settings to make the most of hardware capabilities, to understanding the impact of various apps and updates, this guide provides essential insights for gamers looking to optimize their devices. By mastering these techniques, players can enjoy smoother graphics, faster load times, and an overall enhanced gaming environment, ensuring that their mobile gaming adventures are both enjoyable and competitive.
Climate change has emerged as one of the most pressing issues of our time, influencing various aspects of life on Earth, including agriculture. The agricultural sector, which is vital for food security, livelihoods, and economic stability, is increasingly feeling the adverse effects of climate change. This article aims to explore the multifaceted impact of climate change on global agriculture, analyzing both the challenges and potential adaptation strategies that can be employed to mitigate its effects.
Understanding Climate Change: How To Optimize Your Phone For High-Performance Gaming
Climate change refers to significant changes in global temperatures and weather patterns over time. While climate change is a natural phenomenon, human activities, especially since the Industrial Revolution, have amplified its progression through increased greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs), deforestation, and industrial pollution. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports indicate a rise in global temperatures, with the past decade being the warmest on record.
Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture
Climate change affects agriculture through various channels, including altered rainfall patterns, increased frequency of extreme weather events, shifting growing seasons, and the proliferation of pests and diseases.

Altered Rainfall Patterns
One of the most significant impacts of climate change is altered precipitation patterns. Regions that once enjoyed consistent rainfall may experience prolonged droughts, while others may face excessive rainfall leading to flooding. According to the World Bank, changes in precipitation and temperature are expected to transform agricultural productivity, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. For instance, crops like maize and wheat are highly sensitive to changes in rainfall, which can lead to reduced yields in many areas.
Extreme Weather Events
Climate change is associated with an increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as hurricanes, heatwaves, and droughts. These events can have devastating impacts on agricultural production. A study published in the journal Nature found that extreme weather events have resulted in significant crop yield losses. For example, Hurricane Harvey in 2017 caused substantial damage to Texas agriculture, leading to billions of dollars in losses.
Shifting Growing Seasons
The changing climate is also altering growing seasons. Warmer temperatures can lengthen the growing season in some regions, which might initially seem beneficial. However, these shifts can disrupt established agricultural practices, crop rotations, and pest management strategies. For instance, in the United States, the USDA has reported changes in the timing of planting and harvesting crops, which can affect overall yield and quality.
Pest and Disease Proliferation
With changing temperatures and weather patterns, pests and diseases are likely to become more prevalent in agricultural systems. Warmer climates can facilitate the spread of pests like the fall armyworm and diseases such as blight and rust, which can devastate crops. A report from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) indicated that climate change could increase the incidence of crop pests and diseases, threatening food security worldwide.
Regional Impacts of Climate Change on Agriculture
The effects of climate change on agriculture are not uniform and can vary significantly across regions. Understanding these regional impacts is essential for developing targeted adaptation strategies.
Africa
Africa is considered one of the most vulnerable continents to climate change, with agriculture being a primary source of livelihood for the majority of its population. Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns threaten food security and agricultural productivity. Studies suggest that crop yields in sub-Saharan Africa could decrease by up to 50% by 2050 if no adaptation measures are taken.
Strategies such as climate-resilient crop varieties and improved irrigation practices are essential for mitigating these impacts.
Asia
Asia, home to around 60% of the world’s population, is also significantly affected by climate change. Countries like India and Bangladesh experience monsoon variability, impacting rice and other staple crops. Additionally, rising sea levels threaten coastal agricultural areas through salinization of irrigation water. Implementing integrated pest management and developing flood-resistant crop varieties are critical adaptation measures for this region.
North America, How to Optimize Your Phone for High-Performance Gaming
In North America, climate change poses various risks to agriculture, including changes in precipitation patterns and increased extreme weather events. The Midwest, known as the “Corn Belt,” faces challenges such as increased rainfall leading to flooding and altered growing seasons. Farmers are adopting precision agriculture technologies and practicing sustainable farming methods to adapt to these changes.
Europe
Europe’s agricultural systems are also under threat from climate change, with southern regions experiencing increased droughts and northern regions facing wetter conditions. As farming practices adapt, the EU has implemented policies promoting sustainable agriculture and climate change mitigation to ensure food security.
Adaptation Strategies for Climate Change in Agriculture
Given the myriad challenges posed by climate change, it is crucial for the agricultural sector to develop effective adaptation strategies. Some of the potential strategies include:
Climate-Resilient Crop Varieties
Developing and adopting climate-resilient crop varieties can significantly enhance food security. Biotechnology and traditional breeding methods can be employed to develop crops that are more tolerant to drought, heat, and pest pressures. For instance, drought-resistant maize and flood-tolerant rice varieties have shown promising results in enhancing yield under stress conditions.
Improved Water Management
Efficient water management practices are essential for adapting to altered precipitation patterns. Techniques such as rainwater harvesting, drip irrigation, and the use of drought-resistant crops can optimize water use and enhance agricultural productivity in water-scarce regions.
Sustainable Agricultural Practices
Adopting sustainable agricultural practices can improve resilience to climate change. Practices such as crop rotation, agroforestry, and organic farming not only enhance soil health but also contribute to carbon sequestration, thereby mitigating climate change impacts.
Policy and Institutional Support
Government policies and institutional framework play a vital role in facilitating adaptation in agriculture. Providing farmers with access to climate data, financial assistance, and training on sustainable practices can empower them to adapt to changing conditions effectively. Furthermore, international collaboration and support can help address the global nature of climate change.
Conclusion
Climate change poses substantial threats to global agriculture, impacting food security and the livelihoods of millions around the world. As the effects of climate change continue to unfold, it is imperative for stakeholders in the agricultural sector to embrace adaptation strategies that enhance resilience. By investing in research, promoting sustainable practices, and fostering collaboration among nations, we can mitigate the adverse impacts of climate change and ensure a more secure food future for all.