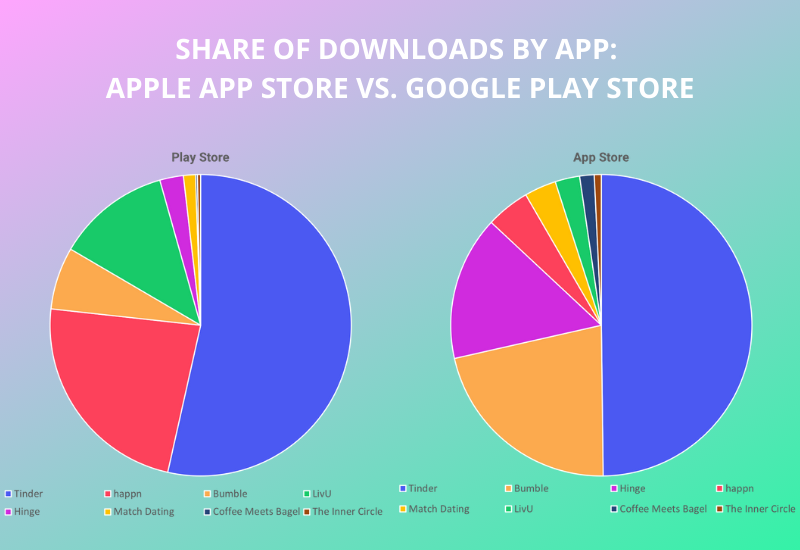
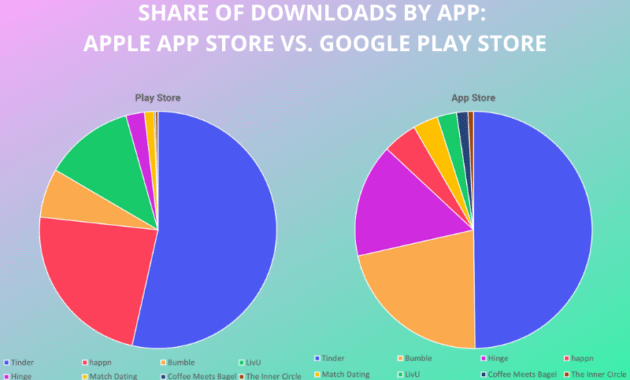
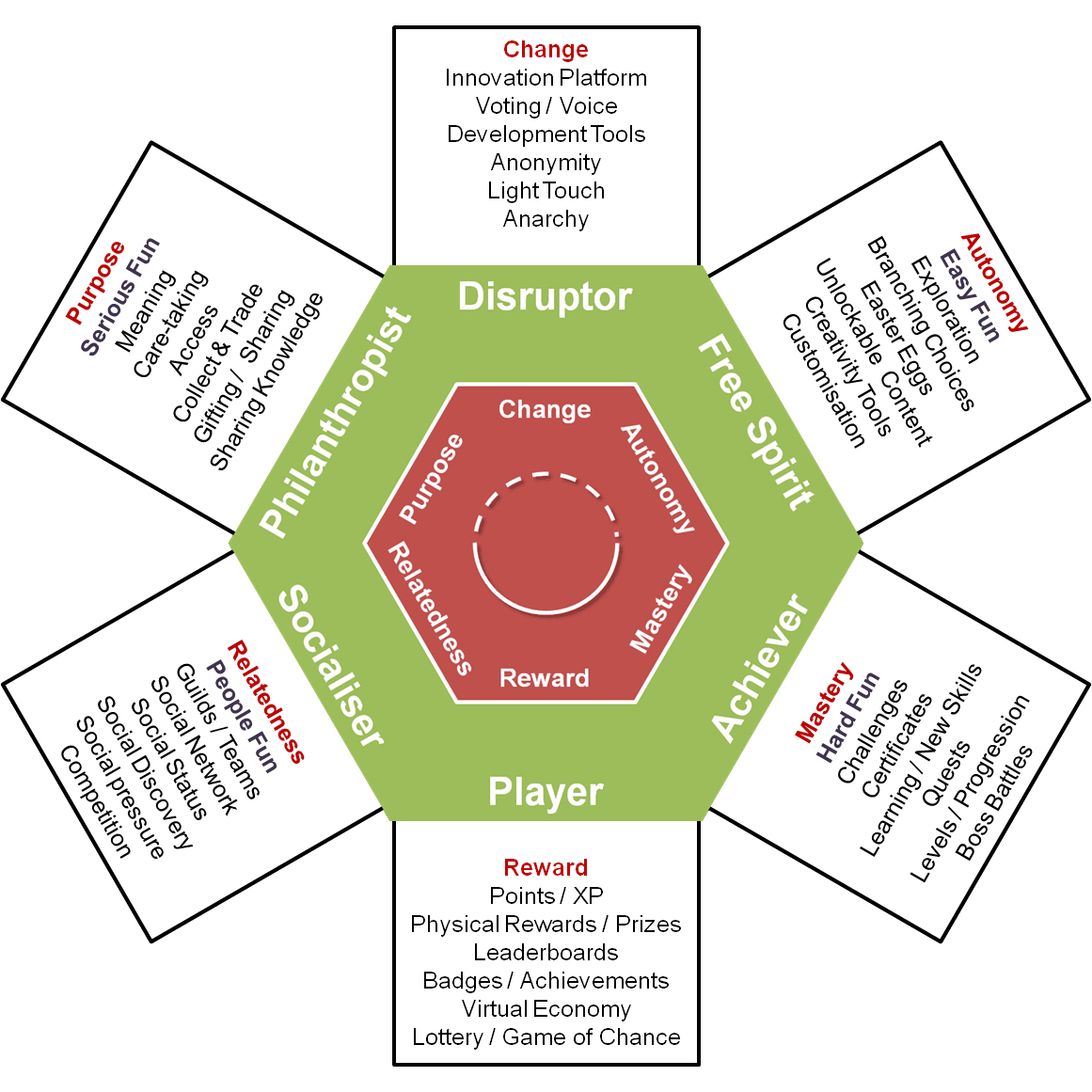
How Gamification Is Changing Online Dating delves into the transformative impact of gamification on the online dating landscape. In this digital era, dating platforms are increasingly incorporating game-like elements to enhance user engagement and interaction. By leveraging features such as rewards, challenges, and point systems, these platforms are not only making the dating experience more enjoyable but also encouraging users to connect in innovative ways.
This evolution reflects a shift from traditional dating methods, as technology introduces new dynamics that influence how individuals perceive and navigate relationships. Gamification serves to bridge the gap between casual interactions and meaningful connections, ultimately reshaping social engagement in the online dating realm.
Climate change is an unequivocal phenomenon that has far-reaching implications for global ecosystems. Over the past few decades, the average global temperature has shown a marked increase, largely attributed to human activities such as fossil fuel consumption, deforestation, and industrial processes. This article explores the various dimensions of climate change and its effects on biodiversity, habitat loss, and ecosystem services.
Understanding Climate Change
Climate change refers to significant alterations in temperature, precipitation, wind patterns, and other elements of the Earth’s climate system. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has consistently reported that the primary driver of climate change is the increasing concentration of greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) are the major GHGs released through human activities.
These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, causing the planet’s temperature to rise, a phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect.
Effects on Global Biodiversity
The implications of climate change on biodiversity are profound. Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, encompassing the diversity of species, ecosystems, and genetic variation. As climate conditions shift, many species are forced to adapt, migrate, or face extinction. According to a study published in the journal Nature Climate Change, approximately one million species are currently at risk of extinction due to climate change and other anthropogenic pressures.
For instance, coral reefs, often referred to as the “rainforests of the sea,” are particularly vulnerable to rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification. The phenomenon of coral bleaching, where corals expel the symbiotic algae living in their tissues, leading to a loss of color and vitality, has been exacerbated by climate change. The bleaching events stress the marine ecosystem, threatening not only the corals but also the myriad species that depend on these ecosystems for survival.
Habitat Loss Due to Climate Alteration
As climate change progresses, habitats that are crucial for various species are disappearing. The alteration of habitats refers to the modification of natural environments, which can occur due to changing climate conditions, human interventions, or both. For example, polar regions are experiencing rapid ice melt due to warming temperatures, which directly impacts species such as polar bears and seals that rely on ice-covered regions for hunting and breeding.
The loss of habitat leads to a decline in populations, diminishing the resilience of ecosystems.
Additionally, temperate forests and grasslands are shifting as climate zones change. Species that have historically thrived in specific climatic conditions may find their habitats unsuitable. This shift not only affects the species directly but also disrupts the broader ecological networks, including food webs and nutrient cycling.
Impact on Ecosystem Services
Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from natural ecosystems, including provisioning services (such as food and water), regulating services (such as climate regulation and disease control), cultural services (such as recreational and spiritual benefits), and supporting services (such as nutrient cycling). Climate change poses a significant threat to these services, as alterations in ecosystems can reduce their ability to provide these essential functions.
For example, changes in precipitation patterns can affect freshwater availability, leading to water scarcity in certain regions. This scarcity not only impacts human populations but also adversely affects agricultural productivity, as crops may suffer from inadequate water supply. Furthermore, the health of ecosystems that regulate local climates, such as forests, is compromised, leading to increased vulnerability of regions to extreme weather events, such as floods and droughts.
Case Studies: Climate Change and Specific Ecosystems: How Gamification Is Changing Online Dating
Several case studies highlight the specific impacts of climate change on ecosystems around the globe. One such case is the Amazon rainforest, which is often referred to as the “lungs of the Earth.” Deforestation, combined with rising temperatures, has led to a decline in the carbon storage capacity of the forest. Studies indicate that ongoing climate change could push large areas of the Amazon into a state of savannization, drastically altering the biodiversity and ecosystem services it provides.
Another significant case is the Arctic tundra, which is experiencing permafrost thawing. As temperatures rise, the frozen ground is beginning to melt, releasing previously trapped GHGs, further exacerbating climate change. This creates a feedback loop that accelerates warming and disrupts local ecosystems, including species that depend on the tundra for survival.
The Role of Conservation and Mitigation Strategies
Addressing the impacts of climate change on ecosystems requires immediate and coordinated conservation efforts. Conservation strategies can include establishing protected areas, restoring degraded habitats, and implementing sustainable land-use practices. Additionally, strategies aimed at reducing GHG emissions, such as transitioning to renewable energy sources and enhancing energy efficiency, are crucial in mitigating climate change and its effects on ecosystems.
The international community has recognized the urgency of these issues, evidenced by agreements such as the Paris Agreement. This global accord aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, thereby reducing the overall risks and impacts associated with climate change.
Conclusion
Climate change is an intricate challenge that demands a comprehensive understanding of its impacts on global ecosystems. The ongoing degradation of biodiversity, the loss of habitats, and the disruption of essential ecosystem services underline the urgent need for action. In light of the evidence presented, it is clear that addressing climate change is not only an environmental issue but a societal imperative.
The fate of ecosystems and the services they provide are inextricably linked to human well-being, necessitating a collective effort to foster resilience and sustainability in the face of climate change.