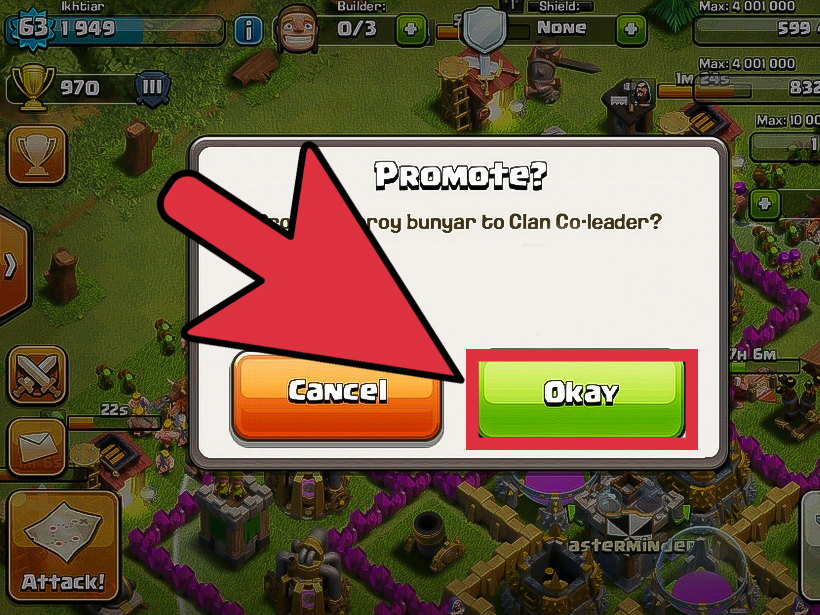
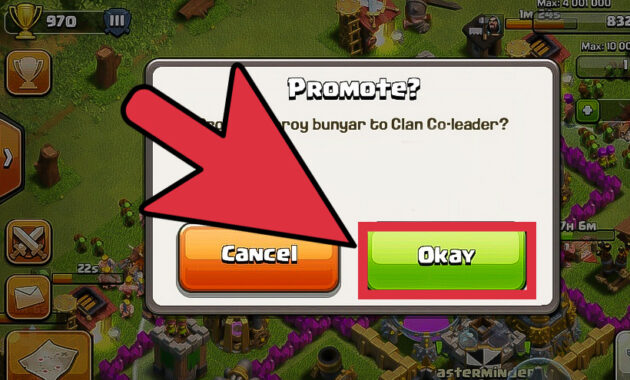
How to Unlock Rare Characters in Brawl Stars is an essential guide for enthusiasts looking to enhance their gameplay experience. This guide not only sheds light on the methods to access rare characters but also highlights the significance of these characters in the overall strategy of the game. Unlocking rare characters can provide players with unique abilities and advantages that enhance their performance in various battles, making understanding the unlocking process crucial for any serious player.
This guide will explore the different ways players can unlock rare characters, including how to earn in-game currency, complete specific challenges, and utilize game events effectively. Additionally, we will discuss the mechanics of character rarity and the strategic importance of each character, offering insights that can dramatically improve your gameplay and allow you to dominate in Brawl Stars.
Climate change is one of the most pressing challenges facing the planet today, with profound implications for ecosystems, biodiversity, and human societies. Among the ecosystems particularly vulnerable to climate change are marine environments, which are home to an immense diversity of species. This article explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, examining the mechanisms through which climate change affects marine life, the consequent ecological ramifications, and potential strategies for mitigation and adaptation.
Understanding Marine Biodiversity
Marine biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms found in oceanic environments, ranging from the smallest microorganisms to the largest marine mammals. It encompasses genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity, which are critical for the resilience and functionality of marine ecosystems. The oceans cover over 70% of the Earth’s surface and host an estimated 230,000 described marine species, with millions more yet to be discovered.
These species play essential roles in the planetary ecosystem, including nutrient cycling, carbon sequestration, and supporting food webs.
Mechanisms of Climate Change Affecting Marine Biodiversity
Several mechanisms associated with climate change impact marine biodiversity. Key among these are rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, sea level rise, and changes in ocean circulation patterns.
Rising Sea Temperatures
Global warming has resulted in rising sea surface temperatures, which can lead to coral bleaching, altered species distribution, and changes in reproductive patterns. Marine species have specific thermal tolerances, and as temperatures rise, some species may be forced to migrate to cooler waters. This shift can disrupt existing ecosystems and lead to loss of biodiversity, particularly for species that are unable to move or adapt quickly.
Ocean Acidification
Increased atmospheric CO2 levels result in higher levels of carbon dioxide being absorbed by the oceans, leading to ocean acidification. This process lowers the pH of seawater, adversely affecting calcifying organisms such as corals, mollusks, and some plankton species. As these foundational species struggle to build their shells and skeletons, the entire marine food web may become destabilized due to the loss of critical habitat and food sources.
Sea Level Rise
Melting polar ice and thermal expansion of seawater contribute to rising sea levels, threatening coastal habitats such as mangroves, salt marshes, and seagrass beds. These ecosystems serve as nurseries for many marine species and provide essential services, including storm protection and carbon storage. The loss of these habitats can lead to a decline in marine biodiversity and alter fish populations and community structures.
Changes in Ocean Circulation Patterns
Climate change affects ocean circulation patterns, which in turn influence nutrient distribution and primary productivity in marine ecosystems. Changes in currents can alter the availability of food for many marine species, leading to shifts in population dynamics and community structure. This can also impact migratory species, such as tuna and whales, which rely on specific currents for feeding and breeding.
Consequences of Declining Marine Biodiversity
The decline in marine biodiversity due to climate change has far-reaching ecological and socio-economic consequences. A decrease in biodiversity can lead to ecosystem instability, making marine environments more vulnerable to additional stressors such as overfishing and pollution.
Ecosystem Services
Healthy marine ecosystems provide a range of services essential to human well-being, including food security, climate regulation, and recreational opportunities. The loss of biodiversity undermines these services, potentially jeopardizing livelihoods, particularly in coastal communities that depend on fishing and tourism.
Food Security
Marine fisheries are a vital source of protein for billions of people worldwide. As fish populations decline due to the impacts of climate change, the availability of fish for consumption decreases, leading to increased food insecurity. Additionally, shifts in fish distributions can affect global fisheries management and exacerbate conflicts over fishing rights.
Impact on Coastal Communities
Coastal communities that rely on marine resources for economic activities are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. The decline of fish stocks and the degradation of coastal ecosystems can lead to economic losses and displacement, increasing the pressure on these communities. Furthermore, social inequalities may be heightened as the most vulnerable populations find it challenging to adapt to changing conditions.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies: How To Unlock Rare Characters In Brawl Stars
Addressing the impacts of climate change on marine biodiversity requires a combination of mitigation and adaptation strategies. Mitigation involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions to limit global warming, while adaptation focuses on enhancing the resilience of marine ecosystems and human communities.
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs)
Establishing and effectively managing marine protected areas (MPAs) can help mitigate the impacts of climate change on marine biodiversity. MPAs provide refuge for vulnerable species, promote biodiversity conservation, and support ecosystem resilience. By reducing other stressors such as overfishing and habitat destruction, MPAs can enhance the capacity of marine ecosystems to adapt to climate change.
Restoration of Coastal Ecosystems
Restoration efforts aimed at rehabilitating coastal ecosystems, such as mangroves, seagrasses, and coral reefs, can enhance biodiversity and improve the resilience of marine environments. These ecosystems play crucial roles in carbon sequestration and provide critical habitat for marine species. Restoration projects can also contribute to community livelihoods by enhancing fish populations and providing protection against storm surges.
Climate-Resilient Fisheries Management
Implementing climate-resilient fisheries management practices is essential to ensure sustainable fish stocks in the face of changing ocean conditions. This includes adaptive management strategies that take into account shifts in fish distributions and changing environmental conditions. Collaborative approaches involving stakeholders, including local fishers and scientists, can facilitate the development of effective management practices that promote sustainability.
Public Awareness and Education, How to Unlock Rare Characters in Brawl Stars
Raising public awareness about the importance of marine biodiversity and the impacts of climate change is crucial for promoting collective action and conservation efforts. Education programs that emphasize the connections between healthy marine ecosystems and human well-being can encourage responsible behavior and support for conservation initiatives.
Conclusion
The impact of climate change on marine biodiversity is a complex and multifaceted issue that poses significant risks to ecosystems and human societies. To safeguard marine biodiversity and ensure the sustainability of marine resources, urgent action is required to mitigate climate change and implement effective adaptation strategies. By prioritizing the conservation of marine ecosystems and promoting sustainable practices, it is possible to protect the rich biodiversity of our oceans for future generations.